4. 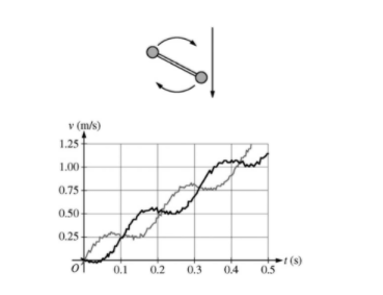
A student on another planet has two identical spheres, each of mass 0.6kg, attached to the ends of a rod of negligible mass. The student gives the assembly a rotation in the vertical plane and then releases it so it falls,as shown in the top figure above. Sensors record the vertical velocity of the two spheres, and the data is shown in the graph of velocity v as a function of time t. Another student wants to calculate the assembly’s angular speed and the change in the linear momentum of the center of mass of the assembly between 0 s and 0.3s. Which of the sequantities can be determined using the graph?